Yeast / Candida Infection: Overview
Alternative names: Candidiasis, Thrush, Oral Thrush, Vaginal Thrush, Candida Albicans, Vaginal Yeast Infection
Candida albicans is an opportunistic yeast that normally inhabits the mouth, throat, intestines and genitourinary tract of most humans and is usually considered to be a normal part of the bowel flora (the organisms that coexist with us in our lower digestive tract). However, it may become pathogenic when there is a disturbance in the balance of flora, or a debilitation of the host from other causes.
- let The Analyst™ find what's wrong
- have a doctor review your case (optional)
- learn what you should be doing right now
Candida can be a difficult condition to diagnose, some treatments are less than effective, and recovery can be prolonged. However, when candida is a problem (whether lab testing confirms it or not) and treatment is effective, there can be great health gains. Attempts at diagnosis are made through questionnaires, analyzing a history of causative factors, blood tests, and stool tests. Some doctors use a questionnaire only because of lab test confusion.
Causes and Development; Contributing Risk Factors
The job of Candida albicans is to recognize and destroy harmful bacteria: Without it, we would be defenseless against many pathogenic bacteria. In a healthy person, Candida albicans numbers in the millions and is controlled by a properly-functioning immune system and "friendly" bacteria.
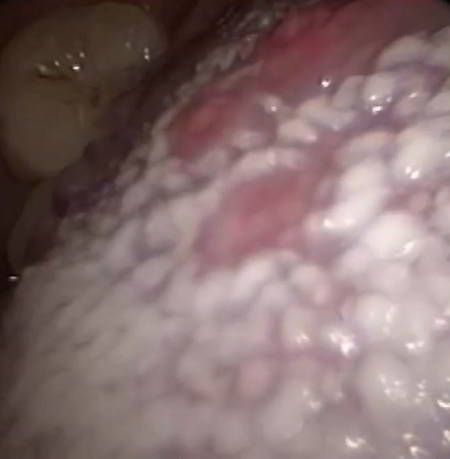
If the number of friendly bacteria is decreased, or the immune system is weakened, or other conditions that favor yeast proliferation occur (diet high in sugar, improper pH in the digestive system) then Candida albicans can shift from yeast form to mycelial fungal form and start to invade the body.
In the yeast state, Candida is a non-invasive, sugar-fermenting organism, while in fungal state it is invasive and can produce rhizoids, very long root-like structures. Rhizoids can penetrate mucosa or intestinal walls, leaving microscopic holes and allowing toxins, undigested food particles and bacteria and yeast to enter the bloodstream. This condition is known as Leaky Gut Syndrome and that is an explanation for many food and environmental allergies.
Transmission
Candida fungi can not become airborne and therefore Candida can not be transmitted by air. Sexual intercourse, deep kissing and oral sex can transmit Candida to/from the genitals or mouth from one person to another. If the other person is healthy, his immune system will destroy Candida cells and prevent infection. However, if his immune system is impaired or he/she eat lots of sugar and carbohydrates then Candida can proliferate.
The most severe cases seem to be associated with the presence of mercury amalgam fillings.
Signs and Symptoms
Early symptoms include itching in the genital area, pain when urinating, and a thick odorless vaginal discharge are frequently present. Candidiasis is unusual in the male and indicates a weakened immune system.
Symptoms of Candida overgrowth are caused by toxins released. Not all listed symptoms will occur in all individuals. Usually, approximately 20 symptoms will be present.
Dysfunctioning Glandular and Organ Symptoms:
- Adrenal and thyroid gland malfunction
- Cold hands or feet
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypoglycemia
- Hypothyroidism
- Impotence
- Low body temperature.
-
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Bloating
- Coating on tongue (oral thrush)
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Dry mouth
- Gas
- Heartburn
- Indigestion
- Inflammation
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Obesity or/and excessive weight loss.
Psychological and Allergic:
- Acne
- Blurred vision
- Bronchitis (recurrent)
- Burning or tingling
- Chemical sensitivity
- Chest pain
- Coughing
- Earaches
- Hay fever
- Headaches
- Hives
- Muscle aches, pain, weakness and tension
- Nasal congestion
- Head tension
- Numbness
- Painful, swollen, stiff joints
- Shortness of breath
- Sinusitis
- Sore throats.
Emotional and Mental:
- ADD, ADHD
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Disorientation
- Drowsiness
- Fatigue
- Feelings of unreality
- Frequent mood swings
- Hyperactivity
- Inability to concentrate
- Insomnia
- Irritability
- Low energy
- Mental confusion
- MS
- Nervousness
- Poor memory.
Skin:
- Acne
- Anal itch
- Athlete's foot
- Dandruff
- Dermatitis
- Dermatitis
- Diaper rash
- Dry skin
- Eczema
- Excessive perspiration
- Facial rash
- Fungal infection of the nails
- Hives
- Impetigo
- Jock itch
- Lupus
- Psoriasis
- Tingling and numbness.
Genitourinary:
- Bladder infection (recurrent)
- Burning on urination
- Cramps
- Cystitis (inflammation of the bladder)
- Endometriosis (irregular or painful menstruation)
- Fluid retention (edema)
- Frequent urination
- Impotency
- Infertility
- Loss of sexual feelings
- Menstrual irregularities
- Painful intercourse
- PMS
- Prostatitis
- Recurrent yeast vaginitis
- Vaginal burning, itching or discharge.
Diagnosis and Tests
Documenting and diagnosing candidal overgrowth can be very confusing as different doctors interpret lab tests differently. Despite this confusion, many people treated properly for a suspected infection improve significantly over time.
Treatment and Prevention
To cure Candida albicans it is essential to find what caused the Candida overgrowth. If the cause is not found and treated, it is possible that treatment will not be effective and/or that Candida will recur.
A comprehensive approach to presumed or documented candida should include:
- Eliminate the chronic use of antibiotics, steroids, immune-suppressing drugs, and birth control pills (unless there is absolute medical necessity).
- Follow the candida control diet suggestions given below.
- Enhance digestion. Check for hypochlorhydria and pancreatic adequacy.
- Enhance immune function. Consider thymus-containing products.
- Enhance liver function.
- Use nutritional and herbal supplements that help control yeast overgrowth and promote a healthy bacterial flora. Many combination preparations are available, and rotating products gives you the opportunity to see which are the most effective and reduces the likelihood of the yeast becoming resistant. Therapy may need to continue for 6 months or longer. Acidophilus supplementation has been shown to be ineffective in candidal infections when used by itself, but can be helpful if a deficiency exists or could be helpful when used in combination with other agents.
Suggested diets are a variation on these basics:
- Avoid sugars. Some doctors strongly recommend you cannot have ANY sugar or grains at all on a program and should also eliminate all fruit until the symptoms resolve. Others are less strict and suggest avoiding foods high in simple carbohydrates such as refined sugars (sucrose, fructose, corn syrup), fruit juices, honey, and maple syrup. Limit intake of high carbohydrate vegetables such as potatoes, corn, yams, and parsnips. How strict you need to be will have to be discovered.
- Avoid foods with a high content of yeast or mold including alcoholic beverages, cheeses, dried fruits, melons, and peanuts.
- Avoid milk and milk products with a high content of lactose.
- Avoid all known or suspected allergic foods.
Foods that can be eaten freely include all vegetables, protein sources (legumes, fish, poultry, and meat), and whole grains. Two to three one-cup servings of the following fruit can be eaten per day as well: apples, blueberries, cherries, other berries, and pears.
Prognosis; Complications
If left untreated, Candida can cause other diseases that may even be lethal, for example by entering the brain or bloodstream. Persons with severely compromised immune system can die from blood poisoning known as Candida Septicemia.
Systemic Candida Overgrowth is a condition that occurs when Candida breaks the intestinal lining and enters the bloodstream. From there, it can travel to various parts of your body and multiply. The symptoms include: muscle aches, sore/stiff joints, fatigue, problems with particular organs, recurrent urinary tract infections, serious illnesses (Asthma, ADHD, Diabetes, MS, Arthritis, CFS, Fibromyalgia).
References and Further Information
Reading a book such as Dr. Crook's The Yeast Connection can be helpful in understanding the condition.
Signs, symptoms & indicators of Yeast / Candida Infection:
Symptoms - Allergy
Symptoms - Bowel Movements
Symptoms - Food - General
 Difficulty swallowing
Difficulty swallowing
If you have fungal overgrowth in your esophagus, symptoms may include pain and difficulty in swallowing.
 Painful swallowing
Painful swallowing
If you have fungal overgrowth in your esophagus, symptoms may include pain and difficulty in swallowing.
Symptoms - Food - Preferences
Symptoms - Gas-Int - General
Symptoms - General
Symptoms - Head - Mouth/Oral
 Coughing up white/yellow curds
Coughing up white/yellow curds
If you have fungal overgrowth in your esophagus, symptoms may include pain and difficulty in swallowing. It is also possible that you may be able to cough up whitish curds that are part of these patches located in your esophagus.
 (Heavily) coated tongue
(Heavily) coated tongue
A white, coated tongue is a sign and symptom of what doctors call Oral Thrush. Candidiasis of the mouth and throat, also known as a "thrush" or oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC), is a fungal infection that occurs when there is overgrowth of fungus called Candida. Candida is normally found on skin or mucous membranes. However, if the environment inside the mouth or throat becomes imbalanced, Candida can multiply. People with white tongues may have painless, white patches in their mouths and throats, but wiping away the white patches will generally cause soreness.
Symptoms - Head - Nose
Symptoms - Metabolic
Symptoms - Mind - General
Symptoms - Nails
Symptoms - Reproductive - General
Symptoms - Respiratory
Symptoms - Sleep
Conditions that suggest Yeast / Candida Infection:
Allergy
Circulation
 Mitral Valve Prolapse
Mitral Valve Prolapse
One doctor has reported that over 80% of the women who have been diagnosed as having mitral valve prolapse suffer from an overgrowth of candida albicans.
Digestion
Female-Specific
 Vulvodynia / Vestibulitis
Vulvodynia / Vestibulitis
Cyclic vulvovaginitis is probably the most common cause of vulvodynia and is believed to be caused by a hypersensitivity reaction to Candida. While vaginal smears and cultures are not consistently positive, microbiologic proof should be sought by obtaining candidal or fungal cultures during a symptom-free phase. The diagnosis of cyclic vulvitis is made based on the patient's report of cyclic symptomatic flare-ups (or, conversely, symptom-free days) and by the patient's report of symptomatic improvement after the administration of long-term topical or systemic anticandidal therapy. [Autoimmunity as a factor in recurrent vaginal candidiasis and the minor vestibular gland syndrome. J Reprod Med 1989;34: pp.264-6]
Infections
Respiratory
Skin-Hair-Nails
 Psoriasis
Psoriasis
A number of gut-derived toxins are implicated in the development of psoriasis including endotoxins (cell wall components of gram-negative bacteria), streptococcal products, Candida albicans, yeast compounds, and IgE or IgA immune complexes. These compounds increase the rate of skin cell proliferation dramatically. Candida albicans overgrowth in the intestines (chronic candidiasis) may play a major role in many cases.
 Male Hair Loss
Male Hair Loss
Candida can cause hair shedding in male or female patients. The exact mechanism is unclear because there are so many possible pathways. The three most likely pathways are thyroid dysfunction, allergies and enzyme suppression.
 Female Hair Loss
Female Hair Loss
Candida can cause hair shedding in male or female patients. The exact mechanism is unclear because there are so many possible pathways. The three most likely pathways are thyroid dysfunction, allergies and enzyme suppression.
Symptoms - Immune System
Symptoms - Liver / Gall Bladder
Risk factors for Yeast / Candida Infection:
Addictions
 Alcohol-related Problems
Alcohol-related Problems
Alcohol kills friendly bacteria, increases toxic overload of the liver and thus allows Candida to grow.
Autoimmune
 Gluten Sensitivity / Celiac Disease
Gluten Sensitivity / Celiac Disease
Genetic disorders such as celiac disease or hemochromatosis can cause Candida overgrowth.
Circulation
 Megaloblastic Anemia / Pernicious Anemia
Megaloblastic Anemia / Pernicious Anemia
Vitamin B12, B6, biotin and folate help maintain candida in its non-invasive form. A B12 deficiency is one of several conditions that can stimulate candida growth.
 Hemochromatosis (Iron overload)
Hemochromatosis (Iron overload)
Genetic disorders such as celiac disease or hemochromatosis can cause Candida overgrowth.
Dental / Oral
Diet
Digestion
 Diarrhea
Diarrhea
Chronic diarrhea can cause the friendly Bifidobacterium bifidum to be expelled from the colon and Candida may then proliferate.
Environment / Toxicity
 General Detoxification Requirement
General Detoxification Requirement
Toxic metals, such as mercury (found in dental amalgams and some fish) and chemicals, such as aspartame, MSG and others can kill friendly intestinal flora, alter immune response and allow yeast to proliferate.
Mental
Nutrients
Organ Health
Parasites
 Parasite Infection
Parasite Infection
Intestinal parasites such as worms destroy friendly bacteria in the gut, making yeast overgrowth possible. It is common for Candida patients to also have parasites and parasites should be suspected if Candida overgrowth recurs.
Supplements, Medications, Drugs
 Broad-spectrum antibiotic use
Broad-spectrum antibiotic use
Antibiotics reduce the number of "friendly bacteria" in the intestinal tract that normally keep the Candida albicans under control.
Symptoms - Food - Intake
Symptoms - Head - Mouth/Oral
Symptoms - Head - Nose
Symptoms - Immune System
Symptoms - Nails
Symptoms - Reproductive - General
Symptoms - Respiratory
Yeast / Candida Infection suggests the following may be present:
Diet
 Consequences of Poor Diet
Consequences of Poor Diet
Improper diets, such as those high in carbohydrates, sugar, yeast and yeast products can lead to Candida overgrowth.
Drug Side-Effect
 (Prescription) Drug Side-Effects
(Prescription) Drug Side-Effects
Steroid hormones, immunosuppressant and anti-inflammatory drugs, ulcer medications or acid blockers used for prolonged periods can all cause yeast overgrowth.
Immunity
 Weakened Immune System
Weakened Immune System
Candidiasis is more common and severe in individuals with weakened immune systems. Any condition that results in a weakened immune system can cause Candida proliferation. Common causes of immune deficiency are AIDS and cancer.
Laboratory Test Needed
Yeast / Candida Infection can lead to:
Digestion
 Increased Intestinal Permeability / Leaky Gut
Increased Intestinal Permeability / Leaky Gut
It is likely that both yeast and bacterial overgrowth commonly occur together; overgrowth of either can lead to Leaky Gut Syndrome.
Musculo-Skeletal
Yeast / Candida Infection could instead be:
Mental
 Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Although psychosis is not a common manifestation of Candida, it has occurred. Mental symptoms have included fatigue, inability to concentrate, depression, mood swings, anxiety, hyperactivity, delusions, "manic depression," psychosis, and suicidal or violent tendencies.
Recommendations for Yeast / Candida Infection:
Amino Acid / Protein
Botanical / Herbal
 Garlic
Garlic
Liberal consumption of garlic, ginger, cinnamon and other aromatic herbs can have significant antifungal activity.
 Grapefruit Seed Extract
Grapefruit Seed Extract
Chronic candidiasis can be successfully treated with grapefruit seed extract according to the many clinics and medical practitioners now prescribing it. Dr Leo Galland, who prescribes it for chronic candidiasis, has reported treatment failure in fewer than 1% of cases, and considers it to be "a major therapeutic breakthrough for patients with chronic parasitic and yeast infections."
 Oil of Oregano
Oil of Oregano
Place 3 drops of oregano oil into an empty gelatin capsule (or vegicap), or mix the same amount of oil into juice and take 3 times each day. Enteric-coated preparations are available at about 50-100mg of oil per capsule or tablet. Several weeks of continuous use may be required for the anti-fungal properties of oil of oregano to clear up a deep-seated Candida infection.
Chemical / Extract
 Boric Acid
Boric Acid
Boric acid in the form of vaginal suppositories is a natural remedy for vaginal yeast infection. Numerous studies prove its superior effectiveness compared to topical and oral antifungal drugs, including drug-resistant cases.
 Caprylic acid
Caprylic acid
Caprylic acid has been shown to be very effective against Candidiasis. Medical literature lists many examples of caprylic acid, and its stabilized salt forms, being used in the successful treatment of Candida infections.
Detoxification
 Supplemental Fiber
Supplemental Fiber
Candidal toxins can be reduced by using a water-soluble fiber source such as guar gum, psyllium seed, or pectin, which can bind to toxins in the gut and promote their excretion.
Diet
 Sugar Avoidance / Reduction
Sugar Avoidance / Reduction
Avoid foods high in simple carbohydrates such as refined sugars (sucrose, fructose, corn syrup), fruit juices, honey, and maple syrup.
 Increased Fruit/Vegetable Consumption
Increased Fruit/Vegetable Consumption
Based on their clinical experience and on very preliminary research, several doctors have suggested that a number of dietary factors may promote the overgrowth of Candida. Dried fruits, which are high in sugar, have been blamed for contributing to promotion of Candida overgrowth. Sugars avoidance is a standard recommendation on any anti-candidal diet.
Digestive Aids
 Probiotics
Probiotics
The use of probiotics to help keep candidal overgrowth from occurring is a common part of many antifungal programs.
Hormone
Laboratory Testing
 Bacteria / Pathogen Testing by PCR
Bacteria / Pathogen Testing by PCR
A Panfungal Panel (Blood or Tissue Biopsy) can test for the presence of several hundred human pathogenic fungal species. This panel also differentiates the Candida genus.
Mineral
Supplements
 GLA (Gamma Linolenic Acid)
GLA (Gamma Linolenic Acid)
GLA can help reduce candida-induced hair loss by suppressing conversion of testosterone to its derivative DHT, in the hair follicles.
Vitamins
 Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
One Osteopath (DO) is known to use intravenous vitamin C followed by intravenous flagyl with good results for candidal overgrowth.
Click to see sample report
Your body is a highly complex, interconnected system. Instead of guessing at what might be wrong, let us help you discover what is really going on inside your body based on the many clues it is giving.
Our multiple symptom checker provides in-depth health analysis by The Analyst™ with full explanations, recommendations and (optionally) doctors available for case review and answering your specific questions.
KEY