Shortness Of Breath: Overview
Alternative names: Dyspnea
Shortness of breath is a frightening feeling of "air hunger" or suffocation brought on by not being able to get enough air.
- let The Analyst™ find what's wrong
- check your overall health status
- have a doctor review your case (optional)
A person may experience shortness of breath even though oxygen levels are within a normal range.
Causes and Development
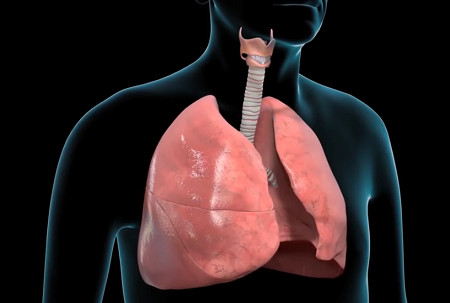
It is natural for a healthy person to become short of breath from strenuous exercise, extreme temperature, or high altitude. There are also many medical causes of shortness of breath, most of which are related to the heart and lungs which form the cardiopulmonary system. Causes of acute shortness of breath include:
- Blockage of the upper airway, for example due to choking or by a tumor
- Anxiety / Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Stress
- Pneumonia (an infection in the lungs)
- Bronchospasm (a temporary narrowing of the airways into the lungs)
- Epiglottitis (swelling of the windpipe)
- Inflammation of lungs after radiation treatment for cancer
- Broken ribs
- Pneumothorax (a collapsed lung)
- Pleurisy (inflammation of the membrane lining the chest)
- Pleural effusion (a buildup of fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest wall)
- Pulmonary edema (excess fluid in the lungs)
- Pulmonary embolism (a blood clot in the lung)
- Pericardial effusion (a build up of fluid around the heart)
- Pericarditis (swelling of the membrane around the heart)
- Heart attack
- Low blood pressure
- Pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the blood vessels of the lungs)
- Sudden massive blood loss
- Hypoxemia (an abnormally low concentration of oxygen in the blood)
- Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning
Causes of long-term (chronic) shortness of breath include:
- Severe obesity
- Asthma
- Lung cancer
- Interstitial lung disease
- Pulmonary fibrosis (scarred or damaged lungs)
- Deconditioning due to lack of exercise
- Sarcoidosis (abnormal collections of inflammatory cells in the body)
- TB (Tuberculosis)
- Arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems)
- Heart failure
- Cardiomyopathy (chronic disease of the heart muscle)
- Anemia (an abnormally low level of red blood cells. which carry oxygen)
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
- Myasthenia gravis
Signs and Symptoms
Breathing difficulty can be described as
- uncomfortable breathing
- an inability to get enough air
- a feeling of breathlessness
- a feeling of smothering, tightness, drowning, or suffocation
Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosing shortness of breath involves identifying the underlying cause. Since there are many possible causes, the first step is a review of the patient's medical history, and a physical examination.
Treatment and Prevention
Aside from treating the underlying cause of shortness of breath, relief of symptoms (palliative care) is very important from the patient's point of view. This includes:
- Receiving extra oxygen
- Increasing ventilation, for example by sitting next to a fan
- Breathing fresh, cool air (lower room temperature, open windows, remove smoke and pet dander from the environment)
- Keeping the head raised (extra pillows in bed)
- Meditation and relaxation
- Increasing the sense of being in an open space (open windows, see a nice view of the outside, be in an empty room)
- Taking anti-anxiety medication
Prevention includes smoking cessation, pollutant/particulate avoidance, losing weight, treating existing medical conditions, and avoiding exertion at high altitude.
Seek medical attention if...
It is important to tell your doctor right away about sudden, severe or worsening shortness of breath. In an emergency situation, shortness of breath is often accompanied by chest pain, fainting or nausea.
On This Page
Shortness Of Breath:Signs, symptoms & indicators of Shortness Of Breath:
Symptoms - Respiratory
Risk factors for Shortness Of Breath:
Circulation
Nutrients
Respiratory
 Pulmonary Fibrosis
Pulmonary Fibrosis
The main symptom of Pulmonary Fibrosis is shortness of breath, with or without exertion, made worse by even slight exertion.
Symptoms - Muscular
 Having excess body fat
Having excess body fat
Thin people in general have less difficulty breathing. If they exercise regularly, they don't breathe hard even during physical activity. Having less fat inside their bodies allows for free expansion of the rib cage and leaves space for the diaphragm to move downward as it should during breathing. Their lungs are also clear of fat, which allows more efficient exchange of oxygen. Almost 70% of bodily waste products are removed in the form of carbon dioxide.
 Being very skinny or being lean or underweight
Being very skinny or being lean or underweight
Thin people in general have less difficulty breathing. If they exercise regularly, they don't breathe hard even during physical activity. Having less fat inside their bodies allows for free expansion of the rib cage and leaves space for the diaphragm to move downward as it should during breathing. Their lungs are also clear of fat, which allows more efficient exchange of oxygen. Almost 70% of bodily waste products are removed in the form of carbon dioxide.
Click to see sample report
Your body is a highly complex, interconnected system. Instead of guessing at what might be wrong, let us help you discover what is really going on inside your body based on the many clues it is giving.
Our multiple symptom checker provides in-depth health analysis by The Analyst™ with full explanations, recommendations and (optionally) doctors available for case review and answering your specific questions.
KEY