Enlarged Spleen: Overview
Alternative names: Splenomegaly
Since the spleen is involved in so many bodily functions, it is vulnerable to a wide range of disorders involving the blood or lymph system, infection, malignancies, liver disease, or parasites. An enlarged spleen is indicative of an underlying medical condition.
- let The Analyst™ find what's wrong
- have a doctor review your case (optional)
- identify any nutritional deficiencies
The spleen is located on the left side of the abdomen and weighs around 200g (8oz) in the average healthy adult. The spleen can be considered a dual-purpose organ: it filters the blood and removes abnormal cells (such as old and defective red blood cells), and it makes disease-fighting components of the immune system (including antibodies and lymphocytes).
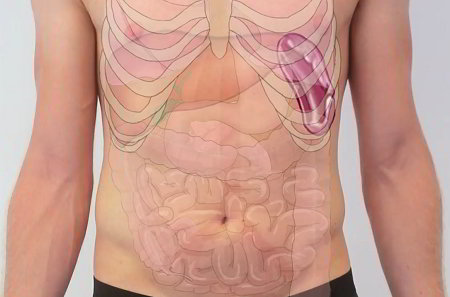
The body of the spleen appears red and pulpy, surrounded by a tough capsule. The red pulp consists of blood vessels (splenic sinusoids) interwoven with connective tissue (splenic cords). The red pulp filters the blood and removes old and defective blood cells. The white pulp is inside the red pulp, and consists of little lumps of lymphoid tissue. Antibodies are made inside the white pulp. Similar to other organs of the lymphatic system, particular immune cells (B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes) and blood cells are either made or matured inside the spleen. Blood enters the spleen via the splenic artery, which subdivides into many tiny branches. Each branch is encased in a clump of lymphocytes, which means every drop of blood is filtered for foreign particles as it enters the spleen.
Hypersplenism is the name given to the condition where the spleen becomes overactive and destroys more blood cells than it should. Symptoms depend on which blood component is lacking. For example, if red blood cells are deficient, anemia will result (with symptoms including fatigue and pallor). Most cases of hypersplenism are caused by disorders somewhere else in the body, such as cirrhosis of the liver.
Splenic rupture can be caused by certain disorders such as infectious mononucleosis: the spleen becomes delicate enough to spontaneously rupture. A sudden blow to the abdomen can split the outer capsule of the spleen and cause bleeding into the abdominal cavity. There are various degrees of splenic rupture. When bleeding is life-threatening, surgery to remove the spleen (splenectomy) is needed.
Incidence; Causes and Development
Splenomegaly occurs in about 10% of systemic lupus erythematosus patients.
A variety of disorders can cause the spleen to enlarge, sometimes to 2kg (roughly 4lbs) or more. Any condition that causes a rapid breakdown of blood cells, such as haemolytic anaemia, can place great strain on the spleen and make it enlarge. This includes:
Infections
Liver Diseases
- Cirrhosis (portal vein obstruction, portal hypertension)
- Sclerosing cholangitis
- Wilson's disease
- Biliary atresia
- Cystic fibrosis
-
- Thalassemia
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Hemolytic anemia due to G6PD deficiency
- Idiopathic autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Immune hemolytic anemia
Cancers
Other causes
- Sarcoidosis
- Sickle cell splenic crisis
- Banti's syndrome
- Felty syndrome
Signs and Symptoms
Although often there are no symptoms, there may be pain in the left upper section of the abdomen. If this pain is present, especially if it is severe or gets worse when taking a deep breath, then medical attention should be sought immediately. An enlarged spleen may also cause a premature feeling of fullness at meals.
Diagnosis and Tests
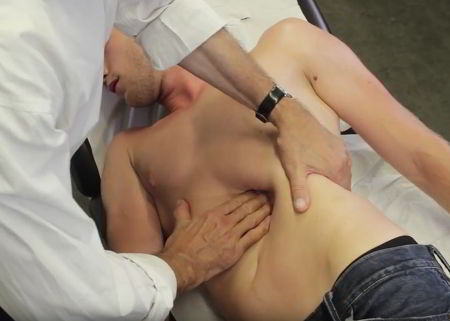
Depending on the condition under investigation, disorders of the spleen can be diagnosed using a number of tests, including:
- Physical examination. A physician will tap along the left-upper quadrant of the abdomen and feel in that same area, especially just under the rib cage.
- Blood tests such as a CBC
- Ultrasound
- Abdominal film or CT scan
- Bone marrow biopsy
- Other tests to check for underlying disorders.
The physician will also ask a series of questions to determine if there are symptoms either from the enlarged spleen or the underlying cause of the large spleen.
Treatment and Prevention
Appropriate limitation of activity, including avoiding contact sports, will help prevent trauma that might cause the spleen to rupture.
Prognosis; Complications
Care will be required for the specific condition causing the splenomegaly.
Rupture of the enlarged spleen is particularly possible in infectious mononucleosis and several other causes of splenomegaly.
On This Page
Enlarged Spleen:Signs, symptoms & indicators of Enlarged Spleen:
Lab Values - Cells
Symptoms - Abdomen
 Moderate/significant/severe epigastric pain or mild epigastric discomfort
Moderate/significant/severe epigastric pain or mild epigastric discomfort
The spleen in located in the upper far left part of the abdomen. Various conditions can cause it to increase in size and cause abdominal pain.
Symptoms - Gas-Int - General
Risk factors for Enlarged Spleen:
Autoimmune
Circulation
 Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive Heart Failure
In severe failure of the right ventricle, elevated venous pressures are transmitted to the portal system, leading to congestion of the spleen and splenomegaly.
Infections
 Infectious Mononucleosis - Mono
Infectious Mononucleosis - Mono
About 50-75% of people with mononucleosis have some spleen enlargement, usually seen two to three weeks after they first become sick. Whether or not the spleen is enlarged, people who have mono should not lift heavy objects or exercise vigorously – especially participating in contact sports – for two months after they get sick, because these activities increase the risk of rupturing the spleen, which can be life-threatening. If you have mono and get a severe sharp, sudden pain on the left side of your upper abdomen, go to an emergency room immediately.
Organ Health
 Hypersplenism
Hypersplenism
Hypersplenism is sometimes referred to as enlarged spleen (splenomegaly), but in fact an enlarged spleen is one of the symptoms of hypersplenism. What differentiates hypersplenism is its premature destruction of blood cells.
Tumors, Malignant
Recommendations for Enlarged Spleen:
Invasive / Surgery
 Surgery
Surgery
A severely ruptured spleen is usually surgically removed. The human body usually adapts well to life without a spleen, so surgically removing a diseased or damaged spleen is possible without causing serious harm to the patient. In some cases, it is possible to remove only the diseased or damaged parts of the spleen, allowing the remaining healthy portions to keep functioning as normal.
Click to see sample report
Your body is a highly complex, interconnected system. Instead of guessing at what might be wrong, let us help you discover what is really going on inside your body based on the many clues it is giving.
Our multiple symptom checker provides in-depth health analysis by The Analyst™ with full explanations, recommendations and (optionally) doctors available for case review and answering your specific questions.
KEY









