Ulcerative Colitis: Overview
Alternative names: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (collective term for Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn's Disease), IBD
This disease typically begins in the sigmoid colon and/or rectum, and then usually progresses until the entire colon is affected. Ulcerative colitis involves only the colonic mucosa, and the lesions are uniform and continuous with no areas of normal tissue interspersed between the diseased mucosa.
- check your overall health status
- identify any nutritional deficiencies
- learn what you should be doing right now
Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are chronic diseases that involve inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. However, ulcerative colitis only affects the colon (large intestine), while Crohn's disease can affect the entire digestive system, from the mouth to the anus.
Incidence
It is seen in both sexes equally, although white and Jewish people are more often affected. A person is five times more likely to get it if one parent has the condition. Peak occurrence is from 15-35 years of age, although any age is susceptible.
Signs and Symptoms
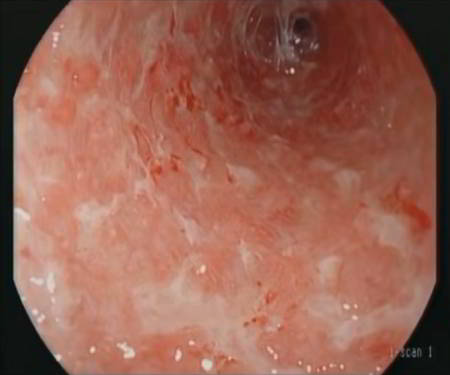
The symptoms of ulcerative colitis occur periodically in flare-ups. During a flare-up, which can come on suddenly and severely, the patient may experience violent diarrhea (typically containing mucus and blood), high fever, abdominal pain, and occasionally peritonitis (inflammation of the lining of the abdominal cavity).
Ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and the rectum and is characterized by chronic inflammation of the entire mucosal layer. About half of patients with ulcerative colitis have mild symptoms which, as well as those listed below, include:
- Increased abdominal sounds
- Diarrhea
- Rectal pain
- Malnutrition
During an endoscopy, severe cases may exhibit signs such as:
- Severe inflammation of the colonic wall
- Extreme edema of the colonic wall
- Complete loss of normal mucosal structure
- Mucosa covered with mucopurulent exudate
- Extensive ulcerations beneath the exudate
Diagnosis and Tests
In order to confirm the diagnosis, testing may include barium X-rays of the upper and lower GI tract, flexible sigmoidoscopy, and sometimes colonoscopy. During these tests, biopsies may be obtained.
Laboratory findings:
- Definitive diagnosis requires a colonic mucosal biopsy
- Normocytic anemia (acute blood loss) or microcytic anemia (iron deficiency due to chronic blood loss)
- Gross or occult blood in stool; WBC in stool
- Leukocytosis during acute exacerbation
- Increased sedimentation rate – indicates active inflammation
- Decreased serum K, NaCl – due to diarrheal loss
- Decreased serum albumin due to loss of protein from the diseased bowel wall; the degree of hypoalbuminemia parallels the severity of the disease
- Increased alkaline phosphatase, SGOT (AST) and bilirubin due to associated liver disease.
Treatment and Prevention
If candida or a bacterial overgrowth is present, further recovery in ulcerative colitis can be achieved by correcting the imbalance through antimicrobial or antifungal agents.
Complications
Ulcerative colitis may also cause secondary problems outside of the colon such as arthritis, inflammation of the eye (posterior uveitis), liver disease (fatty liver, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and primary sclerosing cholangitis), osteoporosis, skin rashes, anemia, kidney stones, carcinoma of the colon, and decreased growth, development, and failure to thrive in children. No one knows for sure why problems occur outside the colon but scientists believe these complications may occur when the immune system triggers inflammation in other parts of the body. Most of these problems are mild and go away when the colitis is treated.
On This Page
Ulcerative Colitis:Signs, symptoms & indicators of Ulcerative Colitis:
Lab Values - Cells
Lab Values - Chemistries
Symptoms - Abdomen
Symptoms - Bowel Movements
 Occasional/frequent mucus in stools
Occasional/frequent mucus in stools
If the disease is limited to the rectosigmoidal area then stools may be normal or dry although there can also be constipation. Rectal mucous, which can be high in red and white blood cells, accompanies stools or occurs between bowel movements.
 Frequent/significant red blood in stools
Frequent/significant red blood in stools
Ulcerative colitis can cause bloody, watery or mucusy bowel movements which may consist only of blood and pus.
 (Very) frequent stools
(Very) frequent stools
Ulcerative colitis may result in an increased urgency to defecate, up to 10 or 20 times per day.
Symptoms - Food - General
Symptoms - Gas-Int - General
Symptoms - Metabolic
Symptoms - Skeletal
Conditions that suggest Ulcerative Colitis:
Autoimmune
 Gluten Sensitivity / Celiac Disease
Gluten Sensitivity / Celiac Disease
Having been diagnosed with celiac disease implies a much lower chance of ulcerative colitis being the explanation for one's symptoms.
Digestion
Environment / Toxicity
 Copper Toxicity
Copper Toxicity
Patients with ulcerative colitis may absorb excess copper in their intestinal tissues which can lead to intestinal disorders, impaired healing and reduced resistance to infections.
Lab Values
 Elevated Homocysteine Levels
Elevated Homocysteine Levels
Several studies have found that patients suffering from inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are more likely to have elevated blood homocysteine levels (hyperhomocysteinemia).
Those suffering from IBD have a much higher risk of both thromboses and osteoporosis. Because elevated blood homocysteine levels are associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis and thrombosis, a team of researchers from McGill University in Montreal explored the idea that homocysteine excess may play an important role in IBD.
To test this hypothesis, they measured homocysteine levels in the plasma of 65 patients with IBD and in 127 healthy controls. Their results revealed a striking difference: The patients with IBD had nearly a six-fold increased incidence of hyperhomocysteinemia (homocysteine levels above the normal range) compared to controls.
About one in every seven patients in the IBD group had hyperhomocysteinemia. As expected, those with vitamin B12 deficiency tended to have higher homocysteine levels. Yet researchers were also surprised to find that 80% of the IBD patients with hyperhomocysteinemia had normal blood levels of vitamins.
This suggests that homocysteine imbalances could be an early warning sign of B-vitamin deficiency inside cells – one that occurs well before vitamin levels actually decline in serum. It is still too early to tell if treating high homocysteine could actually reduce IBD symptoms in patients.
Importantly, as homocysteine levels rose in the patients with IBD, so did the clinical ratings of IBD disease severity, including its length of duration and the use of steroid medications to treat it. [Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 96(7): pp.2143-9]
Skin-Hair-Nails
 Rashes
Rashes
Skin rashes may occur as a result of the presence of ulcerative colitis and disappear when the colitis is treated.
Symptoms - Gas-Int - General
Risk factors for Ulcerative Colitis:
Childhood
 Past and future vaccination or past vaccinations
Past and future vaccination or past vaccinations
Based on a study of 3,545 people who received live measles vaccine as children, their rate of developing ulcerative colitis was 2.5 times higher (3 times higher for Crohn's) compared to an unvaccinated group.
Digestion
 Bacterial Dysbiosis
Bacterial Dysbiosis
A variety of bacterial pathogens can cause severe gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloody diarrhea, fever or abdominal pain. In addition, many of these intestinal microbes can exacerbate or cause flare-ups of symptoms in patients who already have ulcerative colitis.
Family History
 Colitis in family members
Colitis in family members
Crohn's disease affects men and women equally and seems to run in some families. About 20% of people with Crohn's disease have a blood relative with some form of IBD, most often a brother or sister and sometimes a parent or child. A person with one parent who had colitis is five times more likely to have the condition themselves.
Medical Procedures
Mental
 Stress
Stress
Long term stress increases the risk of Ulcerative Colitis flare-ups, according to a study by Susan Levenstein, MD, at the Nuovo Regina Margherita Hospital in Rome. [American Journal of Gastroenterology, May 2000]
Metabolic
Symptoms - Gas-Int - General
Ulcerative Colitis suggests the following may be present:
Autoimmune
Glandular
Ulcerative Colitis can lead to:
Circulation
Diet
Digestion
Eyes / Ocular
 Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis
Ulcerative colitis occasionally causes eye inflammation which resolves when the colitis is treated.
Metabolic
Musculo-Skeletal
 Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Joint inflammation can occur from the overactive immune system seen in ulcerative colitis. This problem may go away when the colitis is treated.
 Osteoporosis - Osteopenia
Osteoporosis - Osteopenia
Scientists believe osteoporosis may occur when the immune system triggers inflammation in other parts of the body. These problems are usually mild and go away when the colitis is treated.
Nutrients
Organ Health
 Cirrhosis of the Liver
Cirrhosis of the Liver
Cirrhosis of the liver can occur when the immune system triggers inflammation there as a result of ulcerative colitis.
 Kidney Stones (Urolithiasis)
Kidney Stones (Urolithiasis)
When the immune system triggers inflammation in other parts of the body because of ulcerative colitis, kidney stones may result. This influence is usually mild and stones may not be a problem once the colitis is treated.
 Fatty Liver
Fatty Liver
Scientists believe a fatty liver can occur when the immune system triggers inflammation in other parts of the body. These problems are usually mild and go away when the colitis is treated.
 Hepatitis
Hepatitis
The immune system may trigger mild inflammation in the liver as a result of ulcerative colitis. This problem is usually mild and goes away when the colitis is treated.
Tumors, Malignant
Recommendations for Ulcerative Colitis:
Botanical / Herbal
 Slippery Elm
Slippery Elm
Slippery elm's soothing mucilage effect has been used for disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. It is part of the herbal combination called "Robert's Formula", which is widely prized by naturopathic physicians for such intestinal inflammations as gastritis, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. For digestive disorders, taking 500-1,000mg of powder tid is often recommended. It may be used in lozenge form as well.
 Boswellia
Boswellia
One small, controlled, double-blind trial has shown that boswellia extract may be helpful for ulcerative colitis. [Eur J Med Res 1997;2: pp.37-43]
 Comfrey
Comfrey
Comfrey has a reputation for promoting healing in stomach ulcers, hiatal hernia and ulcerative colitis.
Diet
 Therapeutic Fasting
Therapeutic Fasting
Short fasts can be beneficial, giving the entire organism an opportunity to restore its cellular and immunogenic integrity.
 High/Increased Fiber Diet
High/Increased Fiber Diet
Approach a high fiber diet cautiously during periods of inflammation, as it may aggravate the condition. As you stabilize, fiber and unrefined foods are important to continue the health of the colon.
A study found Plantago ovata seed (the whole psyllium seed, not just the husk) at 10gm bid to be as effective as the drug mesalamine for maintaining remission in patients with ulcerative colitis. In addition, the Plantago ovata seed may help prevent colon cancer, a common complication of ulcerative colitis, because it increases colonic butyrate levels.
 Food Additive Avoidance
Food Additive Avoidance
It may be wise to avoid the food additive carrageenan, found in various foods such as apple cider, hot dogs, most ice creams and prepared sauces and jellies, as it can produce inflammation and immunodeficiency and has been found to cause colitis and anaphylaxis in humans.
Digestive Aids
 Hydrochloric Acid (Trial)
Hydrochloric Acid (Trial)
It has been suggested that as many as 80% of sufferers have low stomach acid (hypochlorhydria).
 Digestive Habit Changes
Digestive Habit Changes
Foods should be eaten slowly and be well chewed. Eat in a calm atmosphere; do not read or watch television while eating. Any influence that may disrupt good digestion should be avoided.
 Probiotics
Probiotics
Dr. McCann, originally with Kaiser Permanente in Ohio, has pioneered a dramatic, experimental treatment for inflammatory bowel disease which has induced a rapid remission in 16 out of 20 patients with ulcerative colitis. A two-day course of multiple broad-spectrum antibiotics to "decontaminate" the gut is followed by administration of defined strains of E. coli, and Lactobacillus acidophilus to produce a "reflorastation" of the colon. Others have not achieved this same degree of success. It may need to be combined with the specific carbohydrate diet described in the book Breaking the Vicious Cycle.
 Digestive Enzyme (Trial)
Digestive Enzyme (Trial)
Stool analysis or a pancreatic trial will reveal if pancreatic enzymes are necessary.
Drug
Habits
 Tobacco Avoidance
Tobacco Avoidance
Smokers have lower than average rates of ulcerative colitis, but higher than average rates of Crohn's disease. Some patients with ulcerative colitis, in fact, have reported that their disorder began after they quit smoking, and many studies have reinforced the association between smoking and protection against ulcerative colitis. Studies are showing that the nicotine patch helps to induce remission and reduce symptoms in almost 40% of patients who use it for four weeks. Another study found, however, that patches are not useful for maintaining remission. Side-effects, particularly in nonsmokers, include nausea, lightheadedness, and headache. Investigators are studying methods of applying nicotine directly into the colon. (No one should smoke for relief of ulcerative colitis symptoms; the risks from cigarettes far outweigh the potential benefits of their nicotine.)
Hormone
 Hydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone
Ulcerative colitis is both an autoimmune disorder and sensitive to stress. Using hydrocortisol to reduce inflammation followed by physiologic replacement doses when indicated is a reasonable supportive therapeutic strategy.
Laboratory Testing
 Test for Food Allergies
Test for Food Allergies
As many as 50% of sufferers will improve by avoiding food allergens such as dairy, wheat, corn and eggs.
 Test for DHEA
Test for DHEA
DHEA can be a factor in autoimmune problems, which some consider ulcerative colitis to be.
Mineral
Oxygen/Oxidative Therapies
 Ozone / Oxidative Therapy
Ozone / Oxidative Therapy
Rectal insufflation of ozone can hasten tissue repair and kill bacteria that may be slowing the healing process.
Psychological
 Counseling
Counseling
Unresolved grief is sometimes a hidden contributing factor. Resolving the issue as completely as possible may hasten healing and reduce relapses.
Supplements
 Butyrate
Butyrate
Whether by supplement or by enema, pilot studies suggest butyrate is useful in reducing symptoms and restoring indicators of colon health in ulcerative colitis, although one study showed no benefit over placebo. Several doctors claim that many people are helped by butyrate enemas.
Butyrate by enema has substantially reduced the number of bowel movements and amount of bleeding in patients who have not responded to other therapies. This is especially true when the distal colon is involved – an area where the enema can easily reach.
Vitamins
Click to see sample report
Your body is a highly complex, interconnected system. Instead of guessing at what might be wrong, let us help you discover what is really going on inside your body based on the many clues it is giving.
Our multiple symptom checker provides in-depth health analysis by The Analyst™ with full explanations, recommendations and (optionally) doctors available for case review and answering your specific questions.
KEY













